Methodical aspects of coordination and technique training
Childhood is the developmental phase with the greatest learning success. This also applies to coordination training. The earlier children are given the opportunity to test their sensorimotor skills and gain important (initial) movement experience, the better they can realise their potential and the more versatile their technical skills will be. Coordination skills must therefore be promoted at an early age through a variety of learning situations.
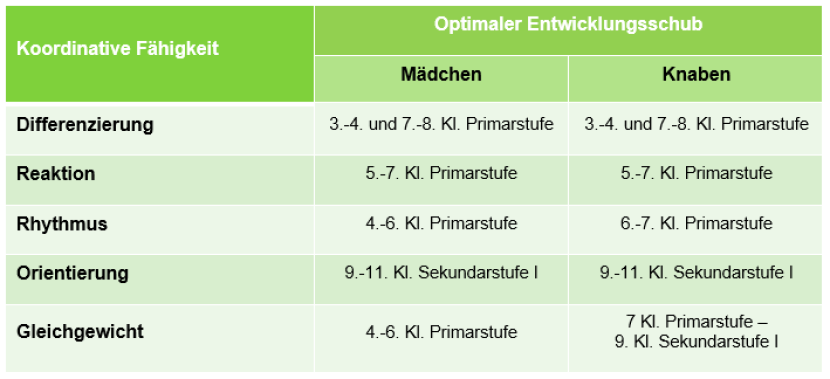
Although the individual components of coordination skills have their greatest developmental boost between the age of seven and puberty, coordination can be trained and improved well into adulthood.
Coordination has a lot to do with a kind of system control; those who can coordinate control their movement behaviour more purposefully. Coordination promises greater certainty of orientation (thanks to order in the system) and therefore also a greater probability of success in terms of creative freedom. The following principles apply to training coordination skills and improving technique:
The principle of constant variation and combination of exercise methods and content applies. The more movement experience gained, the broader the repertoire of coordination patterns, which facilitates the acquisition of new skills.
During training, the learning objectives must be adapted to the individual prerequisites and situational conditions.
The internal and external view of the movement must be reflected (mentally accentuated forms of teaching and learning). The learner's inner perception is more important than the external view.
The learning processes can be optimized and accelerated by cognitive challenges.
Learning new things is easier than relearning, so the right movement patterns must be practiced from the outset.
Only through lifelong learning can the learning and adaptability of the motor control system be maintained. However, it is essential to train coordination skills in good time, during childhood.
Coordination training is not carried out in a fatigued state (which is why, for example, the principle is: coordination training before fitness training).
More Info: