Training rooms / resources
Training rooms (army fitness room)
In addition to the outdoor sports fields (e.g. football pitch, circuit track and other running tracks), the troops have access to a fitness room on the armoury (Wpl), which can also be used in their free time.
A fitness room is basically divided into three areas:
Endurance (cardiovascular/cardio)
Strength (equipment park and free weights area)
Mobility and stability (flexibility/stretching and exercises with your own body weight/simple equipment)
The space required for a fitness facility depends on the equipment and the number of users. Standardised space programmes can therefore hardly be defined and must be adapted to the respective operational objectives and local conditions. Nevertheless, the following information from the civil sector is for information purposes only:
Cardio free space: 20 m2
Cardio devices: 20 m2; min. 4 devices (2 categories; e.g. bike, cross)
Strength equipment: 60 m2; min. 12 pieces of equipment (or strength tower with various stations)
Force free weights: 20 m2
Stretching: 20 m2
The total usable area should not be less than 80 m2. This area can accommodate 12 strength training machines, each with 5 m2 (60 m2) plus a 20 m2 of open space. This minimum area requires existing facilities for endurance sports. Otherwise, at least an additional 20 m2 (4 machines) must be planned for cardio. This results in a minimum size of 100 m2 (Example for gym 200 m2: Cardio 100 m2, Strength 80 m2, Stretching 20 m2 or Cardio 80 m2, power 60 m2, free weight 40 m2, stretching 20 m2). Areas that fall below the minimum size can only be used with restrictions. For space reasons, the free cardio area is often combined with the stretching area in practice.
These figures from the civilian sector are adjusted for a standardised fitness room for the army, as the facility is normally used by a large number of people at the same time. In addition, more emphasis is placed on the mobility & stability zone, as the space required here has increased considerably with modern multifunctional and modular facilities, compared to a simple mat area for mobility training from years gone by. The requirements for an army fitness room are as follows:
Cardio equipment: 40 m2; at least 8 machines (2 categories; e.g. bike, rowing machine)
Strength equipment: 60 m2; at least 12 machines (or strength tower with various stations)
Power free weights: 40 m2
Mobility & stability: 60 m2
A standard fitness room for the Swiss Armed Forces therefore comprises a training area of 200 m2, assuming that approx. 40 people can train at the same time. Only in exceptional cases do we deviate from this concept and work with a reduced room area of 150 m2. In special cases, there is also a variant of a room concept with 100 m2, although this will certainly never come into play at a basic training center.
Endurance (cardiovascular/cardio)
The cardio machines are primarily used for pure endurance training, which is of great importance to health as regular cardiovascular training. As a rule, the individual machines tend to be used for longer periods (45 minutes on average), which is why the machines should be positioned in such a way that training is perceived as pleasant as possible (view of green/training areas or screens). Cardio equipment is also used to warm up before training. The following categories of cardio equipment can be distinguished (* = available on the Wpl):
Bike (bike) *
Rowing machines *
Recumbent (recumbent bike)
Treadmill (treadmills)
Elliptical (cross trainer)
Upper body ergometer (upper body ergometer)
Stepper
Strength (equipment and free weights)
Strength training equipment for guided or partially guided movements is used for general strength training. The variety of these machines is huge. On the one hand, there are various strength training theories with correspondingly designed equipment and, on the other, strength training equipment with a wide variety of resistance systems (weights/plates/discs, springs, pneumatics, hydraulics, levers, electromagnetics). There are machines for training one muscle or muscle group (single-joint exercises) and for training a muscle chain (multi-joint exercises). The 12 basic machines (strength training machines for guided movements) include (* = available on the Wpl):
Lower extremities:
Leg press (leg press) *
Leg Extension (leg extension) *
Leg curl (leg curl; seated or lying down) *
Trunk:
Abdominal (abdominal crunch)
Lower back (back extension)
Upper extremities:
Chest Press *
Shoulder Press *
Lat pull down (back pull) *
Row (rowing pulldown)
Pectoral (butterfly)
Back/Rear Fly (back machine)
Biceps, triceps
The cardio open space can also be used for exercises to strengthen the core (functional gymnastics). The following exercises can be added to the programme:
Lower extremities:
Hip adductors
Hip abductors
Gluteus, possibly calf raiser
Trunk:
Hull torsion
Upper extremities:
Lateral raise
Training with free weights requires good knowledge of the equipment, movement execution, posture and a good understanding of the body. Safety is very important here. The equipment used in the free weight area is numerous. The following overview does not claim to be exhaustive (* = available on the Wpl):
Multi-purpose equipment:
Squat rack (squat rack)
Power Cage
Cable pulls (unguided, but with permanent resistance system):
Lat pull down (upper cable pull) *
Lower cable pull down *
Rowing pull down *
Cross over (crossed ropes)
Triceps tower *
Miscellaneous handles, chains, ropes and attachments *
Benches/own weight:
Adjustable flat bench (with weight rack)*
Horizontal bench (with weight rack)
Negative bench (with weight rack)
Incline bench (with weight rack)
Belly Crunch / Abdominal Board *
Scott bench
Lower back (back stretcher)
Leg lifter *
Dumbbells:
Fist dumbbells 1-10 kg
Dumbbells 4-50 kg *
Discs/bars:
Training pole in various lengths and shapes (diameter 28 mm) *
Competition pole/Olympic pole (diameter 50 mm)
Accessories:
Weight lifting straps
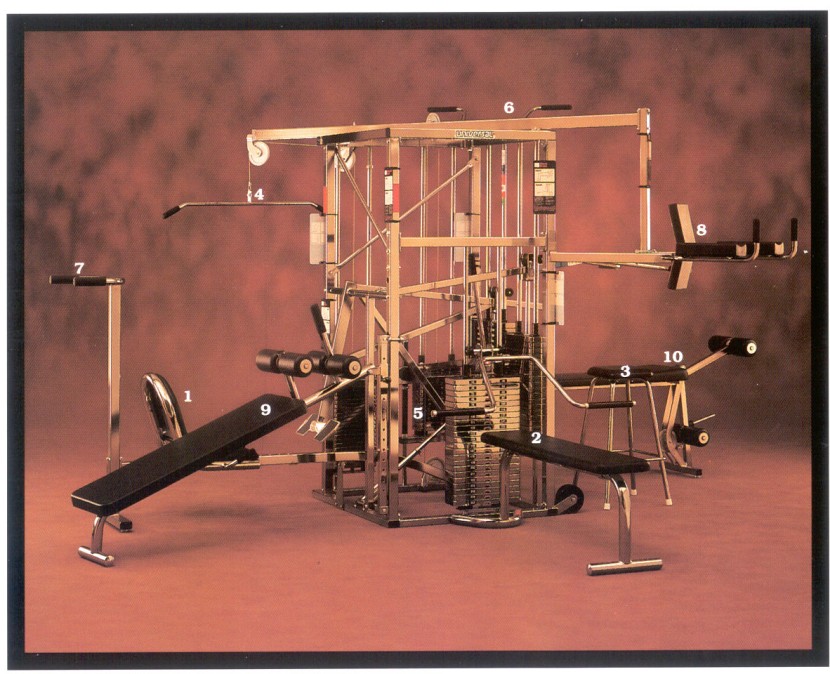
Due to space constraints, many army gyms have a strength tower that includes 10 stations (1 Leg Press, 2 Chest Press, 3 Shoulder Press, 4 High Pulley, 5 Low Pulley, 6 Chinning, 7 Dipping, 8 Hip Flexor, 9 Abdominal Board, 10 Combination Leg Ext/Curl). The tower covers some of the basic exercises mentioned above. Further exercises can be covered with the adjustable flat bench, dumbbells, barbells and the open space also available in the fitness room. The (adjustable) flat bench can be used in combination with the dumbbells, e.g. for the butterfly, with the barbell, e.g. for the chest press, without equipment for core exercises or as a support surface, e.g. for the one-legged squat. If the barbell is used on its own, various exercises (e.g. deadlifts, squats) can also be added.
Mobility & stability
The third area of the fitness room, the open space, is intended for warming up, cool-down/relaxation or mobility training (stretching). This area can of course also be used for strength training or coordination exercises. Countless exercises using your own body weight (supplemented with dumbbells or simple equipment such as the balance board, sling trainer, medicine ball or elastic band) are a useful addition to a training programme. Multifunctional and modular facilities (wall bars/bar bridge with attachment options for applications as well as devices for pull-ups) finally complete the training options in the army gym.
Principles for the use of the fitness room
The army gym is unsupervised, which requires adherence to certain principles:
Use appropriate clothing, shoes and towel
Clean the equipment
Keep order (supply equipment, put weights away)
Master the training/exercise execution. Equipment should be instructed in advance (e.g. RS week 1/2; see Regl. 51.041.01 - Sport in the Armme, material programmes) by a responsible person (C Sport).
Beginners should use strength training equipment with guided movements (more safety). Free weights and barbells are intended for advanced users. There should be two people when training with maximum weights
Music has a motivating effect, but as a matter of courtesy, its use should still be discussed with other gym users.
Training equipment
Muscle training is not necessarily dependent on equipment, as any strengthening exercise can be done with your own body weight. If you want to train a certain muscle group more specifically, increase a training stimulus for a certain purpose or add variety to your training, you can use aids (so-called training aids). We're not just talking about dumbbells here, but a huge range of options such as
Balance board
Balance cushion
Sling trainer
Elasticated rubber band
Exercise stick with elasticated band
Exercise ball
Miscellaneous balls
Weight balls
Weight cuffs
If training is carried out in the sports hall, materials such as ropes, balls, mats and play equipment such as bats or sticks can be integrated as training aids.
Members of the armed forces can easily convert their equipment into training aids on the field in order to vary the strengthening exercises or adjust the level of difficulty. The following military equipment is suitable for training purposes:
Combat rucksack
Helmet
Assault rifle (neutralised)
Pistol (neutralised)