Manifestations of power
Our muscles are capable of different forms of work. They can carry us forwards with endurance when walking, lift an enormously heavy weight once or perform an explosive movement when jumping off the ground. The different forms of labour require different forms of muscle strength and training.
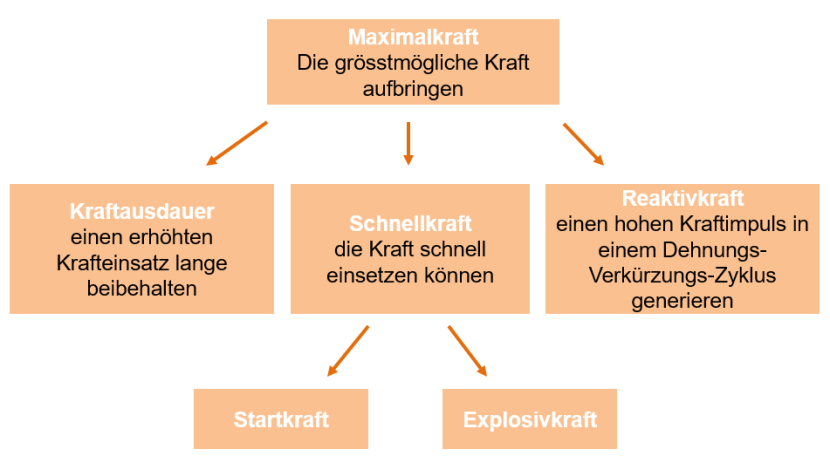
Maximum strength
The maximum force is the greatest possible force that a muscle or muscle group can develop during maximum voluntary activity. The dynamic-concentric and dynamic-eccentric maximum force differ, as more weight can be held during an eccentric, decelerating contraction than is the case with a concentric mode of operation. One measure for measuring maximum strength is the resistance that can be overcome exactly once. The term 1RM (1 repetition maximum) is used for this. For sports in which the body mass has to be carried and accelerated (e.g. climbing, gymnastics, running, ski jumping) or for sports with weight classes, it is advantageous to have a good relative maximum strength (strength in relation to body mass).
Quick power (explosive power, starting power)
Explosive power is the ability to develop as much force as possible in a short time against medium resistance. Resistance is overcome with a high contraction speed in order to accelerate an object or one's own body.
This strength is decisive for performance in many sports because it is often crucial to release as much force as possible in a short time. Speed strength includes two subgroups.
Explosive power is the ability to achieve a rapid increase in power (e.g. take-off in the high jump, weightlifting, throws in athletics).
Starting force refers to a burst of force that can be generated within 30 msec (e.g. surprise action in fencing, deception in game sports, attack in martial arts).
Reactive force
Reactive strength is the ability to quickly and powerfully convert as much force as possible from a dynamic-eccentric contraction into a dynamic-concentric contraction (stretch-shortening cycle) (e.g. box jumps).
Strength endurance
Strength endurance is the organism's resistance to fatigue during prolonged strength performance. The criteria are stimulus strength (as a percentage of the maximum contraction force) and stimulus volume (total number of repetitions). Within the conditional factors, strength endurance belongs to the area of endurance rather than strength.
More info: